What to know before buying an LED system.
Characteristics to take into account about LED lights.
The purchase of an LED system for cannabis cultivation is one of the most valued options by growers, taking into account the savings in energy consumption and many other advantages of LED systems. But to search and find the ideal LED lighting system for your crop, you need to be clear about several concepts about them. Here are some things you should know before buying an LED system. In our online grow shop we tell you everything in detail!
What is LED lighting?
An LED (Lighting Emitting Diode) is a semiconductor diode capable of emitting light. It works by recombining an electron with the hole in the p-n junction region of the device, releasing energy in the form of photons.
Photons are particles of light or other electromagnetic energy that are produced, transmitted and absorbed.
The light we humans see has nothing to do with the light our plants receive, plants use light to feed themselves, mostly known as photosynthesis. Light, water and oxygen are the necessary components for any plant. The vast majority of light bulbs or lamps indicate their power in lumens. The lumen is the unit of measurement designed to measure light visible to the human eye. Seeing that plants receive light in a different way, science developed new light measurement systems, which focus on photosynthetic flux density.
Photosynthetic Photon Flux Density (PPFD) measures the amount of Photosynthetic Photon Flux reaching an area or surface, expressed in micromoles per second per square metre (µmol/s/m2). Values can be affected by the distance between the top of the plant and the light, the type of reflector, the lenses of the luminaire, the reflection of the walls, etc.
Photosynthetic Photon Flux (PPF) measures the flux of photons in the wavelengths that a plant can utilise to process photosynthesis, the range considered for doing so is 400 - 700 Nanometer (nm) measured in Micromoles per second (µmol/s).
The unit for measuring PPF is micromoles per second (µmol/s), and the unit for measuring watts is Joule per second (J/s), so in the numerator and denominator the seconds (s) cancel out, so the unit of measurement becomes micromoles per Joule (μmol/J). The higher the number accompanying these units, the more efficient our system will be at converting electrical energy into photons within the PAR (Photosynthetically Active Radiation).
Types of LEDs.
In the different LED systems we can find several types of LEDs. The most common LEDs that we can find in lighting systems are:
SMD LED.
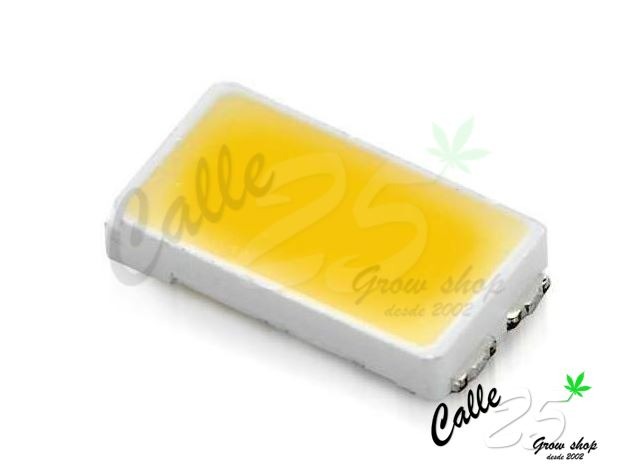
The SMD LED (Surface Mounted Device) are LEDs of excellent quality, they have a very high light output (up to 60 - 70 lumens per watt) together with their low energy consumption, emitting a unidirectional light. In addition, the quality of the light is very high, as is the colour rendering, so we will have very clear colours, improving the quality of our crop. The SMD LEDs are very resistant, if they have blows or falls they will not suffer any damage.
The size of the SMD LEDs is very small (3.5 x 2.8 mm) so the LED lighting systems have a large number of them, so that the light emitted is ideal for the surface required. If one of the SMD LED chips is damaged in an LED system, this will not affect all the others and they will continue to function without any problems.
SMD LED photo.
In Calle25 you can find several LED panels made with SMD LEDs, such as LED Cosmos, LED Kappa 150W, Superstar 60W, LED Aura, Galaxy PRO, LED Zeus 1000W Xtreme CO2...
COB LED.
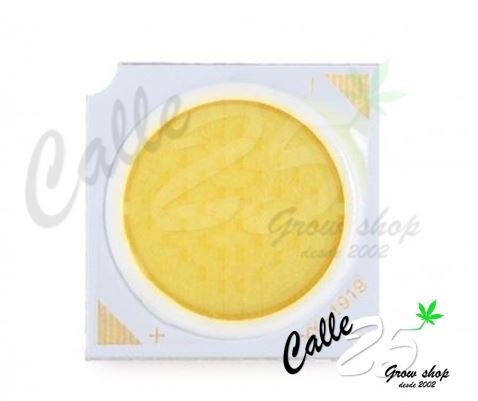
The COB LED (Chip On Board) is a lighting module where only one point of light is visible, but with a higher light output. Like SMD LEDs, they have multiple diodes on the same surface, but COB LEDs have more diodes. As it is a multidirectional LED, we will get a wider angle and therefore a higher light intensity, thus achieving a higher crop yield.
The COB LED has a very good lumen per watt ratio and heat efficiency, thanks to its design and the ceramic cooling substrate in the chips. The light output is up to 120 lumens per watt, double that of SMD LEDs.
LED COB photo.
At Calle25 you can find LED panels made with COB LEDs, such as the Kappa 100W LED System.
Many LED system manufacturers have chosen to combine both types of LEDs, SMD LEDs together with COB LEDs in the same system, such as the Solux Vega LED panel, LED Titan, among others.
Light colour frequencies.
As we have already mentioned, plants need light in order to feed and develop correctly. The colour of the light that the plant receives is very important for this, since after many years of study it has been found out what kind of light colours are more or less favourable, in one phase or another. Plants need LEDs of certain colours, white, blue and red.
White LEDs will simulate brightness and thus provide better growth stimulation.
Blue LEDs will provide UV rays necessary for our plant to achieve a good growth.
Red LEDs are responsible for supplying infrared rays, which are necessary for the plant to develop its flowers.
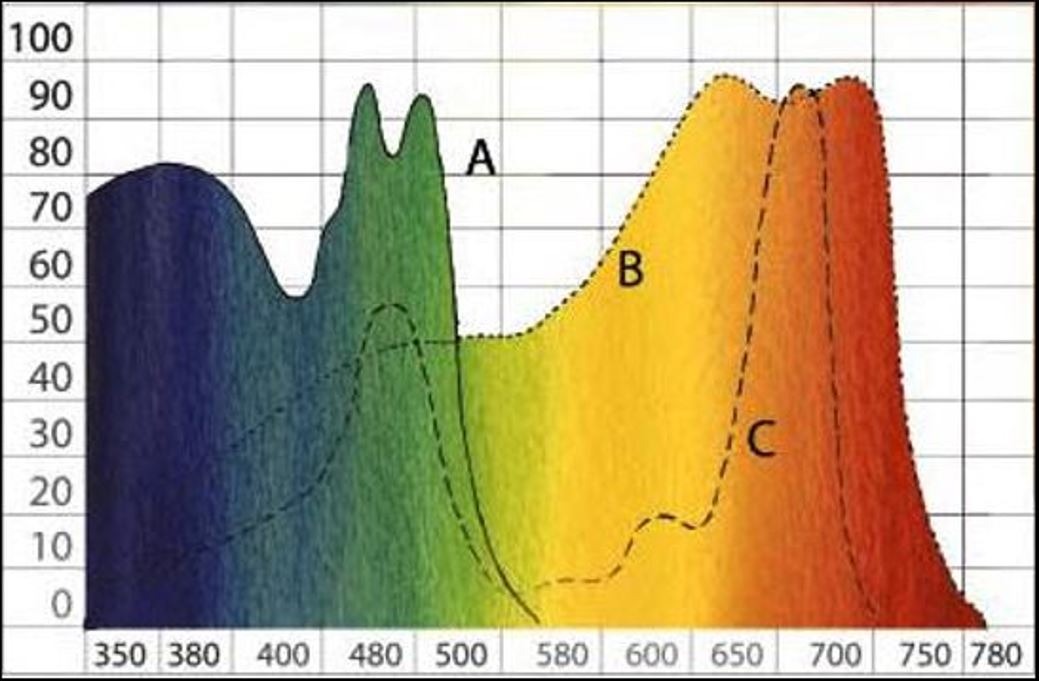
Then we can see a graph where different light spectra can be observed.
In the graph we can see on the left side the relative absorption of light by plants (0 - 100), while at the bottom we see the wavelength, always measured in nanometres (350 - 780).
Wavelength 'A' is the line of the plant's response to photosynthesis.
Wavelength 'B' is the "visible" or human-usable spectrum.
Wavelength 'C' marks the spectrum where plant development is best.
Depending on the number of nanometres the light colour will be one or the other.
380 nm: Ultraviolet light mostly known as UVA. UVA light is very important for resin development, it increases the quantity and quality of the resins. Cannabinoids and terpenes synthesised are determined (among other factors) by UV rays.
Cannabis plants develop a natural defence mechanism to protect themselves from UV rays. This mechanism is the creation of trichomes, which act as photo-protective molecules. Trichomes are molecules that transform ultraviolet rays into less harmful light waves and energy, resulting in large, dense resin layers full of THC, CBD, CBG... to protect against UV rays.
390 - 400 nm: Our plant absorbs photons of light through chlorophyll.
400 - 490 nm: From violet to blue. This is the highest level of photon absorption through the chlorophyll of our plant. The blue colour is the most important for the vegetative growth of our plant. It is a fundamental colour for our plant to grow laterally and to acquire a robust, dense and resistant appearance.
490 - 610 nm: In this range we include green, yellow and orange colours. These are colours where the cannabis plants absorb very little, but penetrate much better into the plant canopy. Thanks to this our plant will have a better metabolism and absorption of nutrients, getting more vigorous and healthy plants.
640 - 720 nm: Red spectrum. This is where cannabis plants have a high absorption of photons. The red colour favours the quantity and quality of the flowering of the plants. In addition, it intensifies the production of the hormone that keeps chlorophyll levels high, transforming the solar/light energy received into glucose (sugars), called meta-topoline.
720 - 740 nm: Infrared or far red. The absorption by the chlorophyll of our plant is low, but it has a very big influence on the growth of roots, lateral branches and increases flowering.
Now that we know how LED systems work, we can compare one LED lighting system with another. If you want to know which LED system you need depending on your growing area, check out our blog post about it.
Still have doubts about changing your traditional lighting system for an LED system? You can visit our blog about the advantages and disadvantages of LED growing.